|
Size: 2140
Comment:
|
Size: 5490
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| #format jsmath |
|
| Line 7: | Line 9: |
| Induction generators require reactive power to establish the field. The customary approach requires capacitors to store field energy, but 2000 km of capacitors capable of briefly moving megawatts per winding is expensive and heavy. I will assume we can supply the VAR (volt-amp-reactive) power from the Halbach arrays on the vehicle sled. For this discussion, assume a 50 meter long Halbach array with 10 centimeter pole-pair pitch, or 500 wavelengths. | Induction generators require reactive power to establish the field. The customary approach requires capacitors to store field energy, but 2000 km of capacitors capable of briefly moving megawatts per winding is expensive and heavy. I will assume we can supply the VAR (volt-amp-reactive) power from the Halbach arrays on the vehicle sled. For this discussion, assume a 50 meter long Halbach array with 10 centimeter pole-pair pitch, or 500 wavelengths. The first and last 5 meters of the sled will be an exciter, feeding kinetic energy from the vehicle to the rotor to establish a magnetic field in rotor and the stator plenums. The last five meters will extract the field energy back out, and into the vehicle sled. The exciter windings will drag on the sled, the extractor windings will pull it, helping maintain the sled in tension. |
| Line 9: | Line 11: |
| How much power? | MoreLater |
| Line 11: | Line 13: |
| The design assumes around 200 KN pushing the vehicle and sled at 30 m/s². For a vehicle accelerating to 10500 m/s (near escape velocity), the drive power will increase from around zero at the start to 2.1 GW, approximately 1850 kilometers eastwards down the track. The "jerk" or change in acceleration might be 10 m/s³, occuring over 3 seconds, at beginning and end. | === How much acceleration power? === |
| Line 13: | Line 15: |
| An additional 1 second "jerk ripple" at the start will test the vehicle's response to acceleration reduction, so the initial acceleration and velocity profile might look like so: | The design assumes around 200 KN pushing the vehicle and sled at 30 m/s². For a vehicle accelerating to 10600 m/s (near escape velocity, plus exit drag), the drive power will increase from around zero at the start to 2.12 GW, approximately 1800 kilometers eastwards down the track. The "jerk" or change in acceleration might be 10 m/s³, occuring over 3 seconds, at beginning and end. |
| Line 15: | Line 17: |
| See FirstTrack for details of initial track acceleration. That results in a vehicle/sled moving at 1000 m/s and 17 km along the track at T=38 seconds. | |
| Line 16: | Line 19: |
| The first 6 km of track will indirectly drive the sled through switching power supplies, up to 300 m/s . This linear motor "mass driver" will be heavy and expensive; power switchers will | MoreLater |
| Line 18: | Line 21: |
| ------ | |
| Line 19: | Line 23: |
| which moves 600 m/s at the start of the main acceleration track | === Multi Layer Model === |
| Line 21: | Line 25: |
| The Halbach arrays on the vehicle sled will have fixed spacings, though they will vary somewhat along the length of the sled. | For a traditional rotary induction motor, the multilayer model approximates field behavior. ''Electromagnetic Power Conversion'' by Levi and Panzer (second edition, Dover, 1974) contains appendix B (pages 465 to 469), ''Determination of the Magnetic Field Associated with a Sinusoidal Current Sheet on the Surface of a Rectilinear Air Gap''. I will modify and simplify this slightly. The model is static; I need to add time dependence. . grumble: The motor literature uses $ \large \tau $ for a half wavelength, rather than the customary $ \large \lambda $ for a full wavelength. I will reluctantly do so here. $ \large \tau $ is also used for circuit time constant. Some mathematicians suggest $ \large \tau $ as a replacement for $ 2 \large \pi $. Also, $ { \large \tau } = {\small { 1 / \sqrt{ 1 - ( v^2 / c^2 ) } } }$ is the length scaling multiplier in special relativity; Laithwaite points out that magnetic effects can be modelled as relativistic Coulomb effects, hence special relativity is worth consideration. Ah well; perhaps a large and extensible set of mathematical emoji is the best long-term answer. The model is an infinite sheet of conductor in the x-y plane, with infinitely permeable material below $ z = 0 $ and above the gap $ z = g $. The planar current density $ K $ (measured in amps per meter in the Y direction) is $ K = K_m \cos( ~ { \large { \pi \over \tau } } ~ x ~ ) $. After some clever math, the Levi/Panzer derivation produces a magnetic potential: $ A_x = { \Large { { \tau \mu_0 K_m } \over \pi } } ~ { \Large { { ~ \cos( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } } ~ y ~ ) } \over { \sinh( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } } ~ g ~ ) } } } ~ \cosh( ~ { \Large { \pi \over \tau } } ~ ( g - z ) ~ ) $ and magnetic fields: $ B_y = ~ \mu_0 K_m ~ { \Large { { ~ \cos( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } } ~ y ~ ) } \over { \Large \sinh( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } } ~ g ~ ) } } } ~ \sinh( ~ { \Large { \pi \over \tau } } ~ ( g - z ) ~ ) ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ $ $ B_z = - \mu_0 K_m ~ { \Large { { ~\sin( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } ~ y ~ ) } \over { \Large \sinh( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } } ~ g ~ ) } } } } ~ \cosh( ~ { \Large { \pi \over \tau } } ~ ( g - z ) ~ ) $ ------ {{ attachment:MLMrotor.png | | width = 800px }} The multilayer model for a six-lobed launch loop rotor can be absurdly simple. The flux wraps around the rotor circumferentially, passing through six open-core stators and six laminated iron cores with a radial rotor "squirrel cage" on each face. Presuming infinite rotor permeability, and given a propagating field in the stator current sheet, we need only consider the induced current in the rotor current sheet, the induced (and resistive) voltage in the stator sheet, and the propagating magnetic field in the vacuum gap between them. Note that only a few hundred meters of the stator is highly energized over the entire launch loop, launching vehicle sleds at altitude or restoring energy with long linear motors on the ground. The pulse power will be huge for a few milliseconds for any given length of rotor or stator. Relatively small amounts of power will be extracted from the rotor to power rotor-to-track electromagnets. MoreLater |
Generator Model
The Launch Loop electrically extracts power from the laminated iron and aluminum winding rotor through aluminum stator windings and delivers it to the Halbach arrays on the magnet sled. The current design has six centimeter-scale stator slots with laminated iron on both sides; this approximates an induction generator 15 centimeters wide.
Accurate modelling of the induction generator requires 3D finite element modelling and experience with error avoidance - simulation tools are garbage in, garbage out. Given the ultra-high rotor speeds, my guess is that slip will be very low, and the stator field will travel forwards at speeds very close to the 12.5 km/s rotor speed.
Induction generators require reactive power to establish the field. The customary approach requires capacitors to store field energy, but 2000 km of capacitors capable of briefly moving megawatts per winding is expensive and heavy. I will assume we can supply the VAR (volt-amp-reactive) power from the Halbach arrays on the vehicle sled. For this discussion, assume a 50 meter long Halbach array with 10 centimeter pole-pair pitch, or 500 wavelengths. The first and last 5 meters of the sled will be an exciter, feeding kinetic energy from the vehicle to the rotor to establish a magnetic field in rotor and the stator plenums. The last five meters will extract the field energy back out, and into the vehicle sled. The exciter windings will drag on the sled, the extractor windings will pull it, helping maintain the sled in tension.
How much acceleration power?
The design assumes around 200 KN pushing the vehicle and sled at 30 m/s². For a vehicle accelerating to 10600 m/s (near escape velocity, plus exit drag), the drive power will increase from around zero at the start to 2.12 GW, approximately 1800 kilometers eastwards down the track. The "jerk" or change in acceleration might be 10 m/s³, occuring over 3 seconds, at beginning and end.
See FirstTrack for details of initial track acceleration. That results in a vehicle/sled moving at 1000 m/s and 17 km along the track at T=38 seconds.
Multi Layer Model
For a traditional rotary induction motor, the multilayer model approximates field behavior. Electromagnetic Power Conversion by Levi and Panzer (second edition, Dover, 1974) contains appendix B (pages 465 to 469), Determination of the Magnetic Field Associated with a Sinusoidal Current Sheet on the Surface of a Rectilinear Air Gap.
I will modify and simplify this slightly. The model is static; I need to add time dependence.
grumble: The motor literature uses \large \tau for a half wavelength, rather than the customary \large \lambda for a full wavelength. I will reluctantly do so here. \large \tau is also used for circuit time constant. Some mathematicians suggest \large \tau as a replacement for 2 \large \pi . Also, { \large \tau } = {\small { 1 / \sqrt{ 1 - ( v^2 / c^2 ) } } } is the length scaling multiplier in special relativity; Laithwaite points out that magnetic effects can be modelled as relativistic Coulomb effects, hence special relativity is worth consideration. Ah well; perhaps a large and extensible set of mathematical emoji is the best long-term answer.
The model is an infinite sheet of conductor in the x-y plane, with infinitely permeable material below z = 0 and above the gap z = g .
The planar current density K (measured in amps per meter in the Y direction) is K = K_m \cos( ~ { \large { \pi \over \tau } } ~ x ~ ) . After some clever math, the Levi/Panzer derivation produces a magnetic potential:
A_x = { \Large { { \tau \mu_0 K_m } \over \pi } } ~ { \Large { { ~ \cos( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } } ~ y ~ ) } \over { \sinh( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } } ~ g ~ ) } } } ~ \cosh( ~ { \Large { \pi \over \tau } } ~ ( g - z ) ~ )
and magnetic fields:
B_y = ~ \mu_0 K_m ~ { \Large { { ~ \cos( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } } ~ y ~ ) } \over { \Large \sinh( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } } ~ g ~ ) } } } ~ \sinh( ~ { \Large { \pi \over \tau } } ~ ( g - z ) ~ ) ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ B_z = - \mu_0 K_m ~ { \Large { { ~\sin( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } ~ y ~ ) } \over { \Large \sinh( ~ { \LARGE { \pi \over \tau } } ~ g ~ ) } } } } ~ \cosh( ~ { \Large { \pi \over \tau } } ~ ( g - z ) ~ )
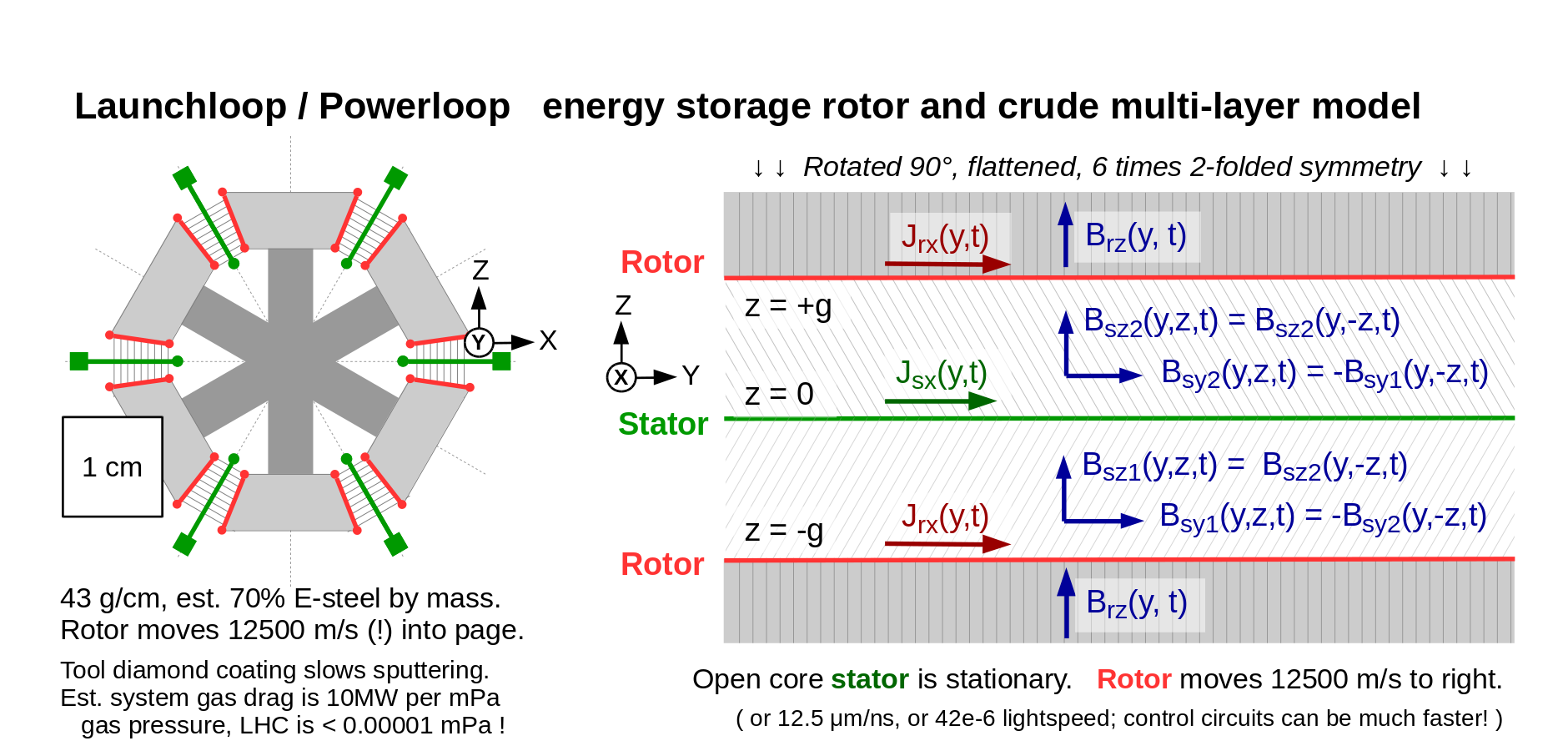
The multilayer model for a six-lobed launch loop rotor can be absurdly simple. The flux wraps around the rotor circumferentially, passing through six open-core stators and six laminated iron cores with a radial rotor "squirrel cage" on each face. Presuming infinite rotor permeability, and given a propagating field in the stator current sheet, we need only consider the induced current in the rotor current sheet, the induced (and resistive) voltage in the stator sheet, and the propagating magnetic field in the vacuum gap between them.
Note that only a few hundred meters of the stator is highly energized over the entire launch loop, launching vehicle sleds at altitude or restoring energy with long linear motors on the ground. The pulse power will be huge for a few milliseconds for any given length of rotor or stator. Relatively small amounts of power will be extracted from the rotor to power rotor-to-track electromagnets.
